Intravenous cannulas, commonly referred to as IV cannula or simply cannulas, are indispensable medical devices used for establishing vascular access in patients. These devices play a crucial role in delivering fluids, medications, blood products, and nutrition directly into the bloodstream, making them essential components of modern healthcare delivery. At GST Corporation Limited (GSTC), we understand the importance of reliable and high-quality IV cannula in ensuring optimal patient care. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of IV cannulas, exploring their features, applications, benefits, and considerations for healthcare professionals.
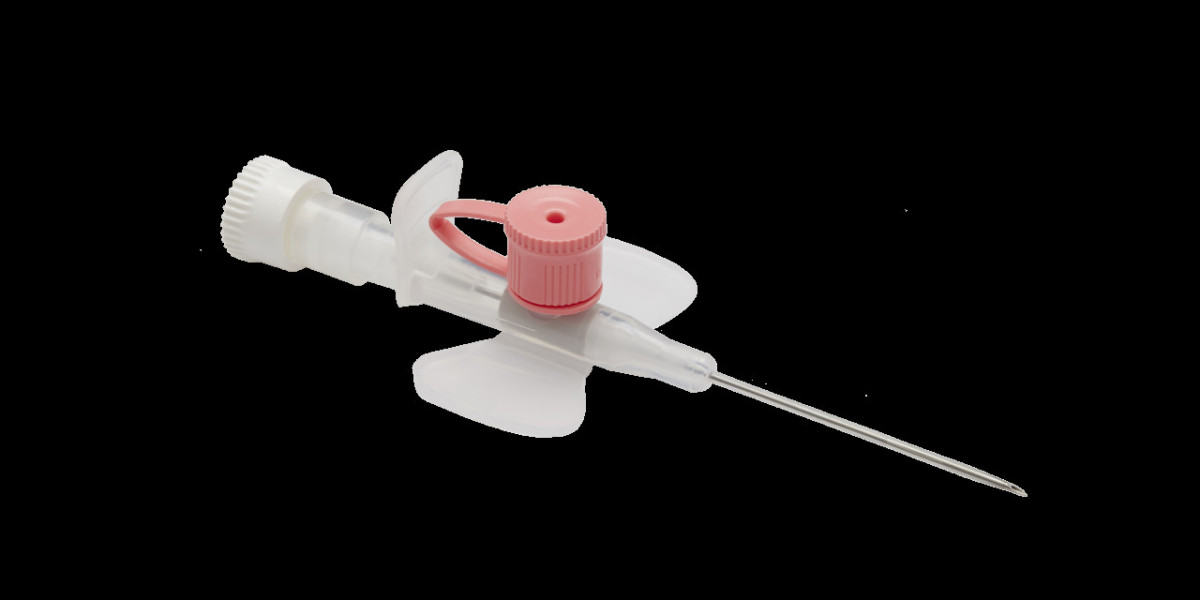
An IV cannula is a thin, flexible tube inserted into a vein to provide access to the bloodstream. It consists of a sharp needle housed within a plastic or metal sheath, which is removed after insertion, leaving the flexible cannula in place. IV cannulas are available in various sizes, ranging from 14 to 24 gauge, with smaller gauge numbers indicating larger diameters.
Additionally, the use of antimicrobial coatings or impregnated materials in IV cannula construction helps reduce the risk of catheter-related infections, promoting patient safety and reducing healthcare-associated costs. Furthermore, research into new materials and manufacturing techniques has led to the creation of ultra-thin and ultra-flexible cannulas that minimize tissue trauma and insertion pain while maximizing patient comfort.
These innovations underscore the ongoing commitment of manufacturers like GST Corporation Limited to advancing the field of vascular access and improving the delivery of care for patients worldwide.
Gauge and Length: IV cannulas come in different gauges and lengths to accommodate various patient populations and clinical needs. Smaller gauge sizes are suitable for fragile veins or pediatric patients, while larger gauges allow for rapid fluid administration in critical situations.
Needle Type: IV cannulas may feature different needle types, including short-bevel, long-bevel, or butterfly needles. Each type is designed to facilitate smooth and atraumatic insertion into the vein, minimizing patient discomfort and tissue trauma.
Winged or Wingless Design: Some IV cannulas come with wings or flanges on either side of the insertion hub, allowing for secure fixation and ease of handling during insertion. Wingless designs are also available for applications where space is limited or patient mobility is a concern. GST Corporation Limited (GSTC), India is a leading Medical Equipment Manufacturer and Exporters of Medical & Surgical devices, rehabilitation Aids & instruments.
Safety Mechanisms: Many IV cannulas incorporate safety features such as retractable needles, needle guards, or passive safety systems to reduce the risk of needlestick injuries and exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
IV cannulas are used across various healthcare settings and specialties for a wide range of clinical purposes, including:
Fluid Administration: IV cannulas are commonly used to administer intravenous fluids, electrolytes, and medications to maintain hydration, correct imbalances, and support patients during surgery, trauma, or critical illness.
Medication Delivery: IV cannulas provide a route for the rapid and precise delivery of medications, including antibiotics, analgesics, chemotherapy drugs, and emergency medications such as epinephrine or naloxone.
Blood Transfusion: IV cannulas facilitate the transfusion of blood products, such as packed red blood cells, platelets, or plasma, in patients with anemia, bleeding disorders, or surgical blood loss.
Diagnostic Testing: IV cannulas allow for the collection of blood samples for laboratory testing, including complete blood counts, electrolyte panels, coagulation studies, and blood cultures.
Parenteral Nutrition: In patients unable to tolerate oral or enteral nutrition, IV cannulas provide access for the infusion of specialized parenteral nutrition solutions containing essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals.
Intravenous cannula are indispensable tools in modern healthcare, providing essential vascular access for fluid administration, intravenous cannula medication delivery, blood transfusion, diagnostic testing, and nutritional support.
At GST Corporation Limited, we are committed to delivering high-quality IV cannula that meet the needs of healthcare professionals and enhance patient care across diverse clinical settings. With advanced features, versatile applications, and a focus on safety and efficacy, our IV cannulas empower healthcare providers to deliver optimal treatment outcomes and improve patient outcomes.
Rapid Access: IV cannulas provide rapid and reliable access to the bloodstream, allowing for the prompt initiation of treatments and interventions in emergencies or critical care settings.
Versatility: IV cannulas are versatile devices suitable for a wide range of clinical applications, from routine fluid administration to complex medication infusions and invasive procedures.
Patient Comfort: Modern IV cannulas are designed for optimal patient comfort, featuring atraumatic insertion techniques, smooth surfaces, and secure fixation methods to minimize pain, tissue trauma, and complications.
Safety: With the incorporation of advanced safety features and adherence to strict infection control protocols, IV cannulas help mitigate the risk of needle stick injuries, bloodborne infections, and other procedural complications.
While IV cannulas offer numerous benefits, their successful use requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
Vein Selection: Healthcare providers must assess the patient's venous anatomy and condition to select the most appropriate site for IV cannulation, considering factors such as vein size, visibility, and accessibility.
Insertion Technique: Proper insertion technique is essential to minimize complications such as infiltration, phlebitis, and nerve injury. Healthcare providers should undergo training and adhere to best practices for IV cannulation to ensure patient safety and procedural success.
Monitoring and Maintenance: Once an IV cannula is inserted, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are necessary to assess for complications, ensure proper function, and prevent catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs). Regular assessment of insertion sites, infusion rates, and catheter integrity is essential for early detection and intervention.
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the design and functionality of IV cannulas. Recent advancements in IV cannula technology have led to the development of novel features aimed at improving patient outcomes and enhancing procedural efficiency. For example, some IV cannulas now incorporate integrated pressure sensors or infusion control devices that allow for precise monitoring and adjustment of fluid delivery rates.